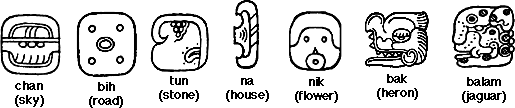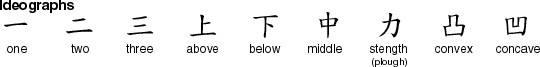Podcast: Play in new window | Download
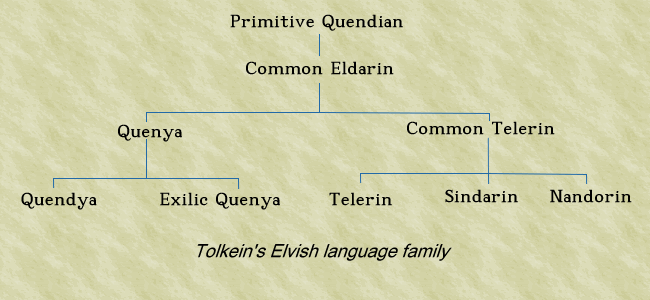
Most people know, or at least have some idea what an alphabet is, but many people might not be so familiar with abjads, abugidas, syllabaries and other writing systems. In this episode I explain what these words mean, and how these writing systems work. I also talk a bit about the history of writing.
Here are some definitions:
Alphabet – a set of letters or other signs, usually arranged in a fixed order, used to represent the phonemes (sounds) of a language [source].

Abjad – a type of writing system where each symbol stands for a consonant, leaving the reader to supply the appropriate vowel [source]. Also known as a consonant alphabet. Long vowels can be indicated by consonants, and short vowels can be indicated by lines, dots and other squiggles added to the consonants letters. When written with the short vowel symbols, they are said to be ‘vocalised’. Normally they are written ‘unvocalised’.

Abugida – a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is secondary [source]. Also known as a syllabic alphabet or alphasyllabary.

Syllabary – a set of written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) moras which make up words [source].

Logograph – a single written symbol that represents an entire word or phrase without indicating its pronunciation [source].
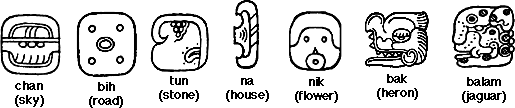
Ideograph – a graphic character that indicates the meaning of a thing without indicating the sounds used to say it [source].
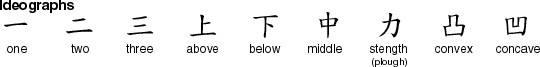
Pictograph – a picture representing a word, phrase, or idea, especially one used in early writing systems. A picture or symbol standing for a word or group of words [source].
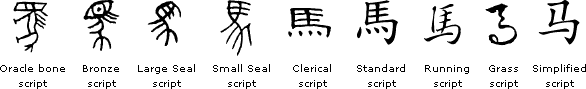
The development of the Chinese character for horse
The tunes featured in the episode are:
The Blackbird’s Tail / Cynffon yr Aderyn Du
The Dragon’s Fancy / Mwmpwy y Ddraig
If you would like to support this podcast, you can make a donation, or contribute to Omniglot in other ways.