Korean is spoken by about 81.8 million people mainly in South Korea and North Korea. The relationship between Korean and other languages is not known for sure, though some linguists believe it to be a member of the Altaic family of languages. Grammatically Korean is very similar to Japanese and about 70% of its vocabulary comes from Chinese.
There are about 50.2 million Korean speakers in South Korea, and about 25.7 million in North Korea. Other countries with significant numbers of Korean speakers include China (2.7 milion), the USA (1.1 million), Japan (998,000), Uzbekistan (250,000), Saudi Arabia (173,000), Canada (153,000) and Australia (109,000) [source].
[top]
Chinese writing has been known in Korea for over 2,000 years. It was used widely during the Chinese occupation of northern Korea from 108 BC to 313 AD. By the 5th century AD, the Koreans were starting to write in Classical Chinese - the earliest known example of this dates from 414 AD. In the 10th and 11th centuries AD they devised three different systems for writing Korean with Chinese characters: Hyangchal (鄕札 / 향찰), Gukyeol (口訣 / 구결) and Idu (吏讀 / 이두). The Gukyeol system first appears in the 11th century, however there is evidence to suggest that it was used from the 7th century AD, or possibly earlier. These systems were similar to those developed in Japan and were probably used as models by the Koreans.
The Idu system used a combination of hanja together with special symbols to indicate Korean verb endings and other grammatical markers, and was used to in official and private documents for many centuries. The Hyangchal system used hanja to represent all the sounds of Korean and was used mainly to write poetry. The Gukyeol system used hanja characters to represent the sounds of Korean.
The Koreans borrowed a huge number of Chinese words, gave Korean readings and/or meanings to some of the Chinese characters and also invented about 150 new characters, most of which are rare or used mainly for personal or place names.
[top]
The Korean Hangeul alphabet was invented in 1444 and promulgated it in 1446 during the reign of King Sejong (r.1418-1450), the fourth king of the Joseon Dynasty. The alphabet was originally called Hunmin jeongeum, or "The correct sounds for the instruction of the people", but has also been known as Eonmeun (vulgar script) and Gukmeun (national writing). The modern name for the alphabet, Hangeul, was coined by a Korean linguist called Ju Si-gyeong (1876-1914). In North Korea the alphabet is known as 조선글 (josoen guel).
The shapes of the consonants are based on the shape the mouth made when the corresponding sound is made, and the traditional direction of writing (vertically from right to left) most likely came from Chinese, as did the practice of writing syllables in blocks.
Even after the invention of the Korean alphabet, most Koreans who could write continued to write either in Classical Chinese or in Korean using the Gukyeol or Idu systems. The Korean alphabet was associated with people of low status, i.e. women, children and the uneducated. During the 19th and 20th centuries a mixed writing system combining Chinese characters (Hanja) and Hangeul became increasingly popular. Since 1945 however, the importance of Chinese characters in Korean writing has diminished significantly.
Since 1949 hanja have not been used at all in any North Korean publications, with the exception of a few textbooks and specialized books. In the late 1960s the teaching of hanja was reintroduced in North Korean schools however and school children are expected to learn 2,000 characters by the end of high school.
In South Korea school children are expected to learn 1,800 hanja by the end of high school. The proportion of hanja used in Korean texts varies greatly from writer to writer and there is considerable public debate about the role of hanja in Korean writing.
Most modern Korean literature and informal writing is written entirely in hangeul, however academic papers and official documents tend to be written in a mixture of hangeul and hanja.

A recording of the Korean consonants by Jessica Kwon
The double consonants marked with * are pronounced fortis. There is no symbol in IPA to indiciate this.
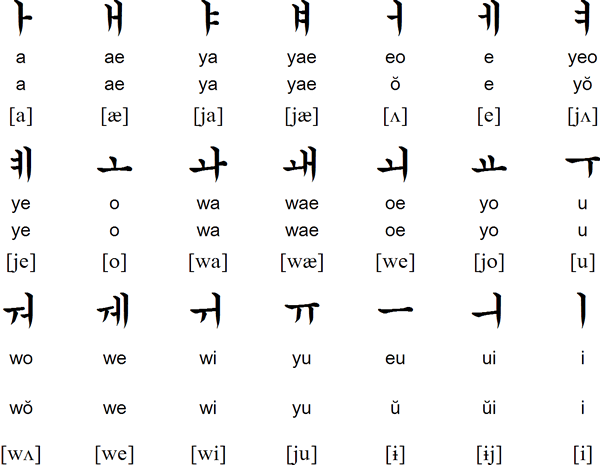
Download a Korean alphabet chart in Excel, Word or PDF format.
A recording of the Korean vowels by Jessica Kwon
See the Korean alphabet pronounced:
[top]
The earliest romanization systems for Korean appeared in the early 19th century. It is thought that Philipp Franz Von Siebold, a German doctor based in Japan, developed the first one in 1832. Other systems were created by missionaries and scholars from England, France, Canada and Japan during the 19th century and early 20th century. In 1933, the Korean Language Society promulgated The Unified Han'gŭl Orthography System, the first romanization system created in Korea by Koreans.
There are now official systems in both South Korea and North Korean, however many Koreans continue to spell their names in their own ways. For example, the second most-common surname in Korean, 이, is written Lee, I, Yi, Ye, Ri or Rhee in South Korean. In North Korea, it is written 리, and romanized as Ri. Historically, it was written 니 [李] (Ni). It means plum, and is also the 4th most-common surname in China, where it is pronounced lǐ in Mandarin and lei5 in Cantonese. It is romanized as Li, Lee, Lei or Lie.
Romanization systems currently in use include:
Information about Korean Romanizaiton
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Romanization_of_Korean
Korean Romanization Converter
http://roman.cs.pusan.ac.kr/input_eng.aspx
[top]



Modeun Ingan-eun Tae-eonal ttaebuteo Jayuroumyeo Geu Jon-eomgwa Gwonrie Iss-eo Dongdeunghada. Ingan-eun Cheonbujeog-euro Iseong-gwa Yangsim-eul Bu-yeobad-ass-eumyeo Seoro Hyungje-ae-ui Jeongsin-euro Haengdongha-yeo-yahanda.
Modŭn in'ganŭn t'aeŏnal ttaebut'ŏ chayuroumyŏ kŭ chonŏmgwa kwŏllie issŏ tongdŭnghada. in'ganŭn ch'ŏnbujŏkŭro isŏnggwa yangshimŭl puyŏbadassŭmyŏ sŏro hyŏngjeaeŭi chŏngshinŭro haengdonghayŏya handa.
Motun inkanun thayenal ttaypwuthe cayulowumye ku conemkwa kwelliey isse tongtunghata. inkanun chenpwucekulo isengkwa yangsimul pwuyepatassumye selo hyengceyayuy cengsinulo hayngtonghayeya hanta.
A recording of this text by Jessica Kwon
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)
Information about Korean | Phrases | Numbers | Colours | Time | Dates | Family words | Tongue twisters | Tower of Babel | Articles | Learning materials | Links | Learn Korean with 90Day Korean [affiliate link]
[top]
Information about the Korean language
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Korean_language
https://www.mustgo.com/worldlanguages/korean/
https://www.90daykorean.com/learn-korean/
https://www.britannica.com/topic/Korean-language/Linguistic-characteristics
Online Korean lessons
http://rki.kbs.co.kr/learn_korean/lessons/e_index.htm
http://www.langintro.com/kintro/
http://www.learnkorean.com/
http://www.lifeinkorea.com/Language/korean.cfm
http://hangulforest.com/index_e.htm
http://www.korean-course.com
http://korean.cuk.edu/en/
http://ilovelanguages.org/korean.php
http://domandhyo.com
https://www.learn-korean.net
https://www.optilingo.com/blog/category/korean/
https://hangulbeuja.com/
http://www.koreanclass101.com/
Learn to read, write and pronounce Korean letters
https://avatalks.com/tools/character/character-character-ko
Learn Korean with Glossika
Find Korean Tutors with LanguaTalk
Korean courses and other resources available on Amazon
A-chik Tokbirim, Adinkra, ADLaM, Armenian, Avestan, Avoiuli, Bactrian, Bassa (Vah), Beitha Kukju, Beria (Zaghawa), Borama / Gadabuursi, Carian, Carpathian Basin Rovas, Chinuk pipa, Chisoi, Coorgi-Cox, Coptic, Cyrillic, Dalecarlian runes, Elbasan, Etruscan, Faliscan, Fox, Galik, Georgian (Asomtavruli), Georgian (Nuskhuri), Georgian (Mkhedruli), Glagolitic, Global Alphabet, Gothic, Greek, Hurûf-ı munfasıla, Irish (Uncial), Kaddare, Kayah Li, Khatt-i-Badíʼ, Khazarian Rovas, Koch, Korean, Latin, Lepontic, Luo Lakeside Script, Lycian, Lydian, Manchu, Mandaic, Mandombe, Marsiliana, Medefaidrin, Messapic, Mongolian, Mro, Mundari Bani, Nag Chiki, Naasioi Otomaung, N'Ko, North Picene, Novo Tupi, Nyiakeng Puachue Hmong, Odùduwà, Ogham, Old Church Slavonic, Oirat Clear Script, Ol Chiki (Ol Cemet' / Santali), Old Italic, Old Nubian, Old Permic, Ol Onal, Orkhon, Osage, Oscan, Osmanya (Somali), Pau Cin Hau, Phrygian, Pollard script, Runic, Székely-Hungarian Rovás (Hungarian Runes), South Picene, Sutton SignWriting, Sunuwar, Tai Viet, Tangsa, Todhri, Toto, Umbrian, (Old) Uyghur, Wancho, Yezidi, Zoulai
Page last modified: 13.08.25
[top]
You can support this site by Buying Me A Coffee, and if you like what you see on this page, you can use the buttons below to share it with people you know.

If you like this site and find it useful, you can support it by making a donation via PayPal or Patreon, or by contributing in other ways. Omniglot is how I make my living.
Note: all links on this site to Amazon.com, Amazon.co.uk
and Amazon.fr
are affiliate links. This means I earn a commission if you click on any of them and buy something. So by clicking on these links you can help to support this site.
[top]