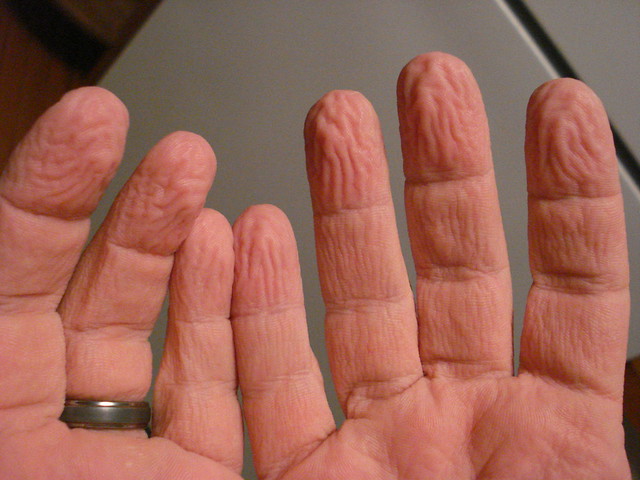
If your hands and fingers become quobbled, should you be worried?
Quobbled is an dialect word from Wiltshire in the south west of England that means wrinkly – so there would be no need to worry, it’s just a temporary phenomenon.
According to Words and Phrases from the Past, quobbled is defined as:
quobbled, adj. of a woman’s hands: shrivelled and wrinked from being too long in the washtub (English dialect)
Another definition is found in A Glossary of Words Used in the County of Wiltshire
By George Edward Dartnell, and Edward Hungerford Goddard (1893):
quobble. n. and v. After being a long while in the washtub a woman’s hands are apt to get ‘all in a quobble,’ or ‘ter’ble quobbled,’ that is, shrivelled and drawn and wrinkled up.
In Joseph Wright’s 1903 book, The English dialect dictionary, being the complete vocabulary of all dialect words still in use, or known to have been in use during the last two hundred years; founded on the publications of the English Dialect Society and on a large amount of material never before printed. (they really went in for short, snappy title back then), we find:
quobble, v. Of water: to make a noise in boiling
Then there’s:
quob, sb. and v.
1. A marshy spot; a bog, quagmire; a quicksand.
2. all of a quob, in a mess; in a heap; a bad bruise
3. an unfirm layer of fat
4. A throb; a palpitation
5. v. To quiver like jelly; to throb, to palpitate
Related words include:
- quobby = marshy, boggy, flabby, wanting solidity
- quobmire, sb. a quagmire
Apparently quob comes from the East Friesian kwabbeln / kwobbeln (to tremble, vibrate). This is probably related to the West Frisian word kwab (weak, blubbery mass of fat or flesh; very fat person; brain lobe; jellyfish) [Source], and the Dutch word kwabbig (flabby, squishy) [Source]
Some other interesting words from Wiltshire dialect include:
- dumbledore / dumble = the humble-bee
- gigletting = fond of rough romping; wanton
- lottle = to sound as water trickling in a small stream
- muddle-fuss = a persistent meddler with other people’s affairs
- to womble = to wobble about from weakness
Source: A Glossary of Words Used in the County of Wiltshire.