
Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?

Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?
What do the words font and police have in common?
Well, a font or typeface as used in computers and other electronic devices is called a police [pɔ.lis] or police de caractères in French.

As well as meaning font, police also means policy, branch or department. It comes from the Italian word polizza (policy, bill, voucher), from the Medieval Latin apodissa (receipt for money), from the Byzantine Greek *ἀπόδειξα (*apódeixa), from Ancient Greek ἀπόδειξις (apódeixis – proof, publication, demonstration). The English word policy comes from the same root [source].
The word police, as in the forces of law enforcement, comes from the Middle French police (governance; management), from Latin polītīa (state, government), from Ancient Greek πολιτεία (politeía – citizenship, government, adminstration), from πολῑ́της (polī́tēs – citizen) [source].
Another French word for font, and also melting, smelting, thawing and
cast iron, is fonte [fɔ̃t]. This probably comes from fondre (to melt (down), smelt, dwindle), from the Old French fondre, from the Latin fundere (to melt), from fundō (I melt), from the Proto-Italic *hundō (pour out), from the Proto-Indo-European *ǵʰewd- (to pour) [source].
The word font, as in “a receptacle in a church for holy water, especially one used in baptism”, comes from the Latin fōns/fontis (fountain), possibly from the Proto-Indo-European *dʰenh₂- (to flow) [source]. The name of the River Danube comes from the same root, via the Latin Dānubius, from the Proto-Celtic *Dānowyos, from *Dānu, from the Proto-Indo-European *déh₂nu (river goddess) [source].
What are your favourite fonts?
The other day the word onderwerp [ˈɔndərwɛrp] came up in one of my Dutch lessons. It means subject, topic or issue, and to help me remember it, I decided to look into its etymology.
It comes from onder (under, among) and werpen (to throw, shed, cast), and is a calque of the Latin word subiectum (that which is spoken of, the foundation or subject of a proposition) [source].
Related expressions include onderwerpen (to subject), onderwerping (submission, subjugation, subjection), onderwerpszin (subject clause), gespreksonderwerp (topic of conversation, talk, conversation piece), nieuwsonderwerp (news item)
Subiectum comes from subiciō (throw under or near; supply; forge; subject; propose), from sub- (under) and iaciō (throw, hurl). The English word subject comes from the same root, as do related words in other languages, such as sujet (subject, cause, reason) in French, and soggetto (subject, dependent) in Italian [source].
So an onderwerp and a subject is something that is thrown under.
A related Dutch word is voorwerp [ˈvoːrˌʋɛrp], which means object or item, and comes from voor (for, before, in front of) and werpen (to throw, shed, cast), and is a calque of the Latin word obiectum (a charge, accusation), which is the root of object comes from the same root, as do related words in other languages, from obiciō (throw to; offer, present) [source]

Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?
What would you call a knitted woolen hat with a bobble on top?
I would call it a bobble hat, and I discovered yesterday that in French such a hat is called un bonnet à pompons or un chapeau à pompons or simply un bonnet. What about in other languages?
Bonnet [bɔ.nɛ] also means hat, cap, beanie, knit cap, skully, stocking cap or (bra) cup. Other types of bonnet include:
A bigwig, or “person of consequence”, is un gros bonnet, and the French equivalent of six of one, half a dozen of the other is bonnet blanc, blanc bonnet.
Bonnet comes from the Middle French bonet, from the Old French bonet (material from which hats are made), from the Frankish *bunni (that which is bound), from the Proto-Germanic *bundiją (bundle), from the Proto-Indo-European *bʰendʰ- (to tie).
The English word bonnet comes from the same root, and can refer to various types of headgear, particularly a type of hat usually framing the face and tied with ribbons under the chin and worn mainly by females.
In Scots a bonnet/bunnet refers to “A head covering for men or boys, including all kinds of caps, but not hats”.
Sources: ReversoDictionary, Wiktionary, Dictionaries of the Scots Language / Dictionars o the Scots Leid
An interesting Dutch word I learnt yesterday is liflafjes [ˈlɪf.lɑf.jəs], which
means scraps, trimmings, leftovers or knickknacks [source]. The singular version, liflafje, apparently means “a small meal that fails to fill” or “a trifle” and is a diminutive of liflaf, which means insipid food, insipid text(s) or bland writing, and used to mean insipid or tasteless [source].
According to webwoordenboek.nl, liflaf means “een smakelijk maar weinig voedzaam gerechtje” (a tasty but not very nutritious dish), or “een aardig maar overbodig iets” (a nice but unnecessary thing).
These words come from liflaffen, a dated word that’s used mainly in Belgium to mean to grovel, fawn, flatter, caress or fondle. A related word is liflafferij [ˌlɪf.lɑ.fəˈrɛi̯], which means flattery or sweet-talking [source].
A knick(-)knack is a small ornament of minor value, a trinket or bauble. It is a reduplication of knack (aptness, petty contrivance, trick), which possibly comes from the Middle English krak (a sharp blow). An equivalent in Dutch is snuisterij [source].
A mishmash is a collection containing a variety of miscellaneous things. It is a reduplication of mash. Some synonyms include hodgepodge, melange, mingle-mangle, oddments and odds and ends. Do you have any others? An equivalent in Dutch is mikmak [source].

Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?
I came across an interesting Dutch word today – snorfiets [snɔrfits], which sounds like ‘snore fits’, and means a moped or scooter, particularly one limited to a maximum speed of 25 km/h (15.5 mph) [source].
Snor [snɔr] on its own means mustache or whiskers, and when I saw snorfiets I thought it maybe referred to a bicycle with mustache-shaped handlebars, or some other mustache-shaped parts. In fact it comes from snorren (to hum, roar, purr, whirr).
Fiets [fits] means bicycle, and its origins are uncertain. It may be named after Elie Cornelis Viets, a wheelwright from Wageningen who made and repaired bicycles from 1880. It may be an abbreviation of a Dutch version of the French word velocipède, or it might come from vietse/fiette, Limburg and East Brabant dialect words meaning ‘to run fast or move quickly’, or from the older dialect word vietsen (to move quickly). The last exclamation is thought to be the most likely [source].
Bicycles, or fietsen, are quite popular in the Netherlands, so much so that there are more bikes than people there. According to an article in The Brussels Times, in 2018 there were an estimated 22.9 million bicycles in the Netherlands, and just 17.2 million people, or 1.3 bicycles per person.
Other types of fiets include:

Here’s a recording in a mystery language.
Do you know or can you guess the language, and do you know where it’s spoken?
I discovered the other day the the exclamation mark (!), which is apparently known as an exclamation point in American English, has a number of other names. When it was first introduced by printers in the 15th century, it was known as a sign of admiration or exclamation or the note of admiration in English.
In the early 20th century it was known as an ecphoneme [source]. A related word is eroteme, which is another name for the question mark (?), and comes from the Ancient Greek ἐρώτημα (erṓtēma – question), from ερωτώ (erotó – to ask) [source].
In 1950s American typesetting manuals it was referred to as a bang. Related punctuation marks are the interrobang (‽), a combination of an exclamation mark and question mark that was invented in 1962 by Martin K. Speckter, an American advertising executive [source], and the gnaborretni (⸘), an inverted interrobang [source].
Printers might call it a screamer, gasper, slammer or startler.
British hackers apparently call it, or called it, a shriek or pling, which is my favourite name for this punctuation mark.
In Welsh the exclamation mark is known as a ebychnod, from ebychu (to exclaim) and nod (mark), or rhyfeddnod, from rhyfedd (strange, odd) and nod.
In Armenian the equivalent of the exclamation mark (see below) is known as a Բացականչական նշան (Bats’akanch’akan nshan) or “exclamatory mark/sign” or “screamer”.
Here are some exclamation marks in other alphabets:
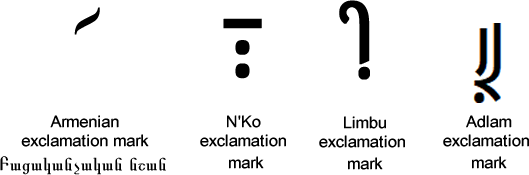
What is the exclamation mark called in other languages?
Here’s a video I made last week about the word exclamation: